Millimetron
Millimetron space observatory (Spektr-M) is a project of Astro Space Center of Lebedev Physical Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences (ASC LPI).
⚡️ Introduction
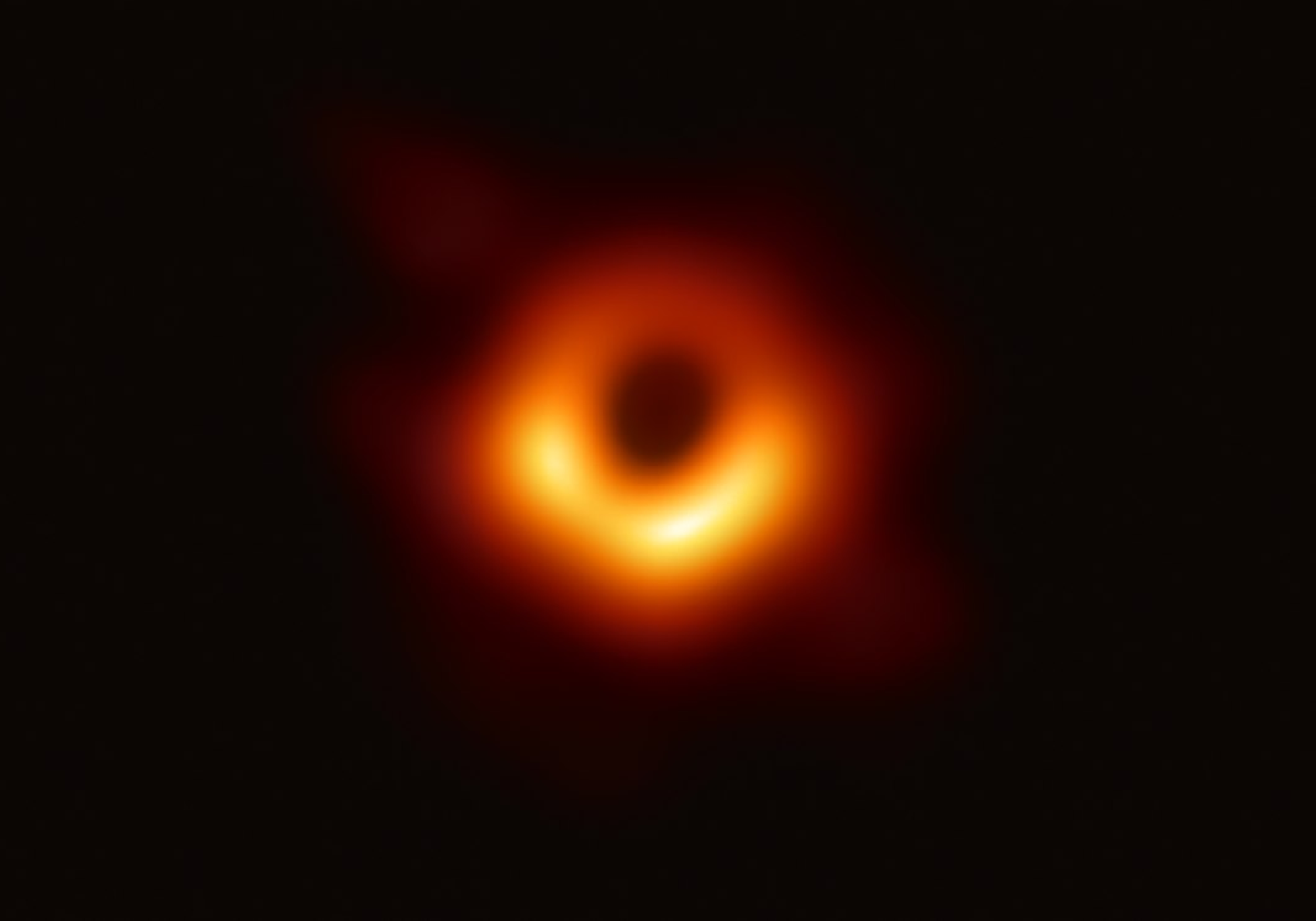
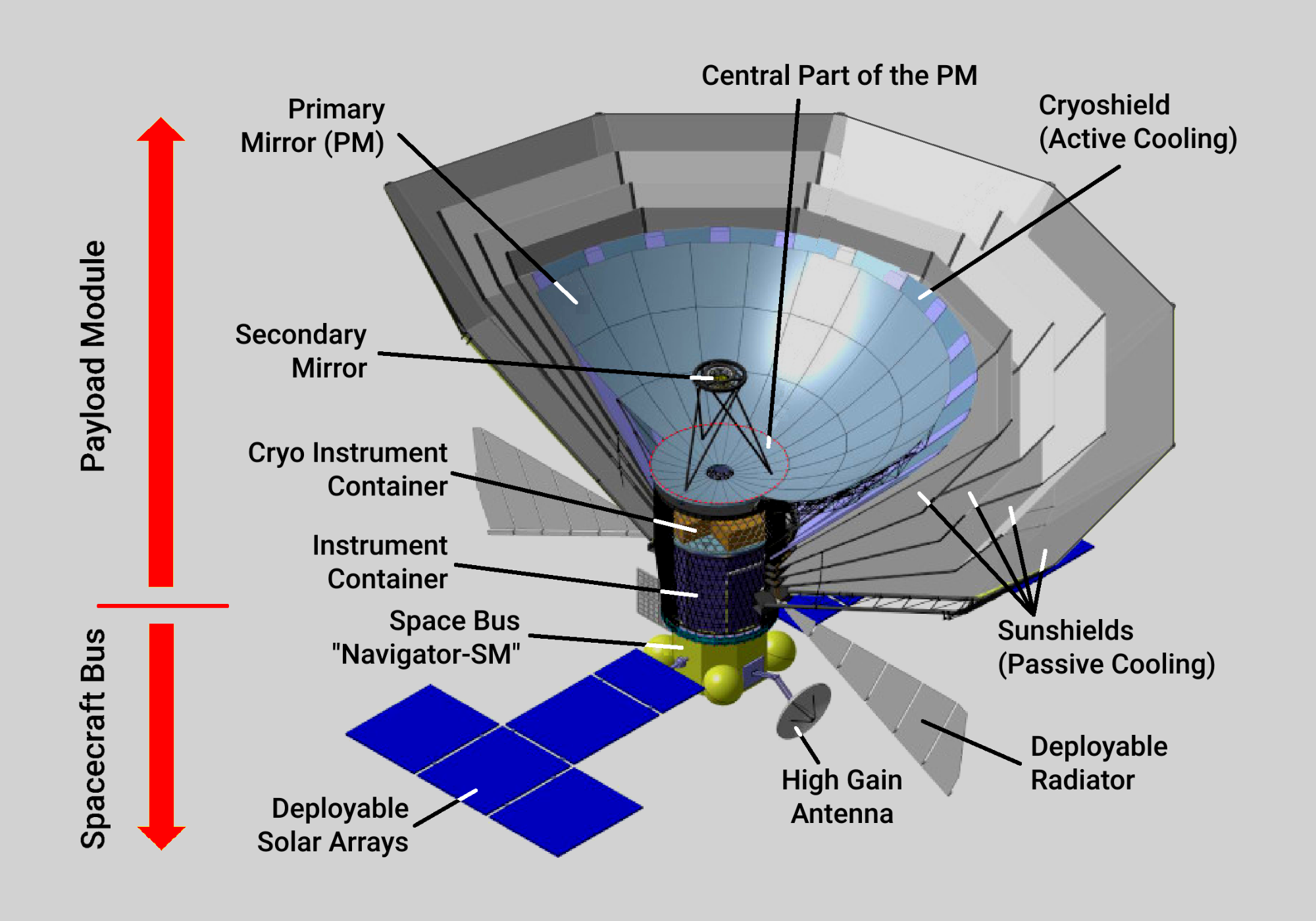
Millimetron Space Observatory (“Spektr-M”) (Fig. 1) is a project of Astro Space Center of Lebedev Physical Institute, Russian Academy of Sciences (ASC LPI). It will be a 10-meter deployable and cooled space telescope designed to study various objects in the Universe at millimeter and infrared wavelengths from 0.07 to 10 mm. The observatory has two operational modes: as single-dish and as the space VLBI station in a Space-Earth interferometer. The first mode will have the best sensitivity to study the weakest sources of the Universe. The second mode together with ground telescopes will provide high angular resolution up to 10−8 - 10−9 arcseconds to study the structure of the most compact objects in the Universe - supermassive black holes (Fig. 2).
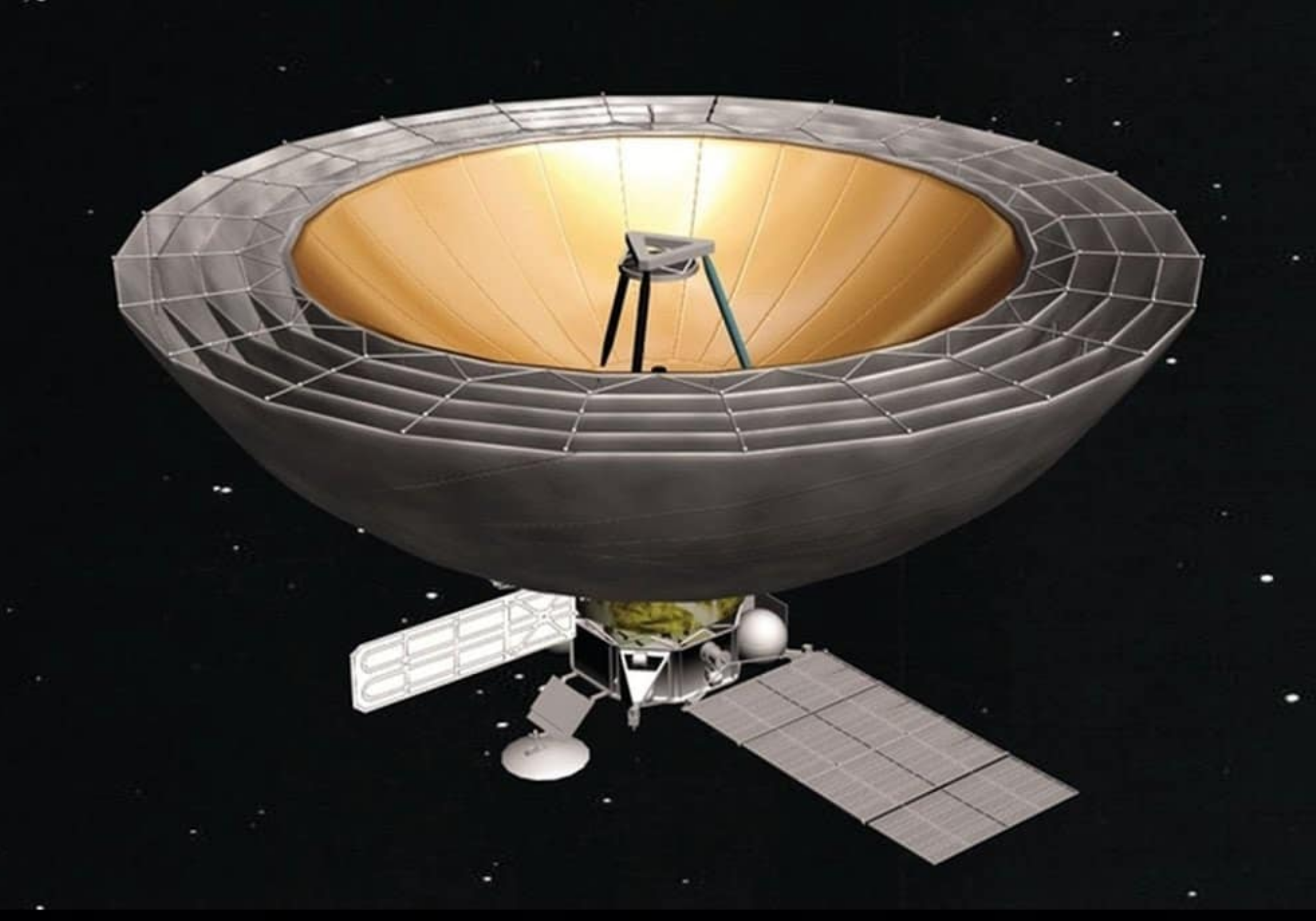


Deep cooling of the telescope mirror system and scientific payload enables the high sensitivity (Fig. 3). While, high angular resolution is provided by the orbit configuration. Initially the observatory will be located near the Lagrange point L2 at a distance of 1.5 million kilometers from Earth in the anti-solar direction and in the second phase of the mission will operate in a near-Earth high elliptical orbit (HEO). Scientific program of Millimetron space observatory is aimed to solve a set of the most important and breakthrough scientific problems in the field of modern astrophysics and cosmology, including amongst others detailed studies of black hole shadows, search for wormholes, water trail in the Galaxy, CMB spectral distortions. The Millimetron Space Observatory project is approved by Russian Space Agency and included in the Russian Federal Space Program for 2016-2025 years.
⚡️ VLBI Instruments
Quote from the official website of the Millimetron project:
Millimetron Space-Ground VLBI receivers will be used for Very Long Baseline Interferometry observations between Millimetron and ground stations such as ALMA, NOEMA, EHT network, KVN network and so on. Observations will utilize both Lagrange L2 point as well as elliptical near-Earth orbit. For efficient operations, VLBI instruments will be split into frequency bands, matching those of ALMA and other ground based stations. For multi-frequency operations capability, all VLBI bands will be quasi-optically combined using the set of dichroic filters and will receive signal from the same direction on the sky.
“Contact-Technologia” NPP, LLC has developed and manufactured the entire hardware complex of technical means for the ground tracking station of the international radio astronomy project Radioastron (“Spektr-R”). Using successful experience, we started working on one of the most important parts of the scientific equipment of the Millimetron project. The main device of which is an Analog-to-Digital Converters and Formatters (“Formator-P”). The device “Formator-P” is intended for scientific data acquisition and buffering, formatting scientific data according to predefined frame structure, and transferring resulting high-speed digital data stream to downlink transmitter device (Fig. 4).
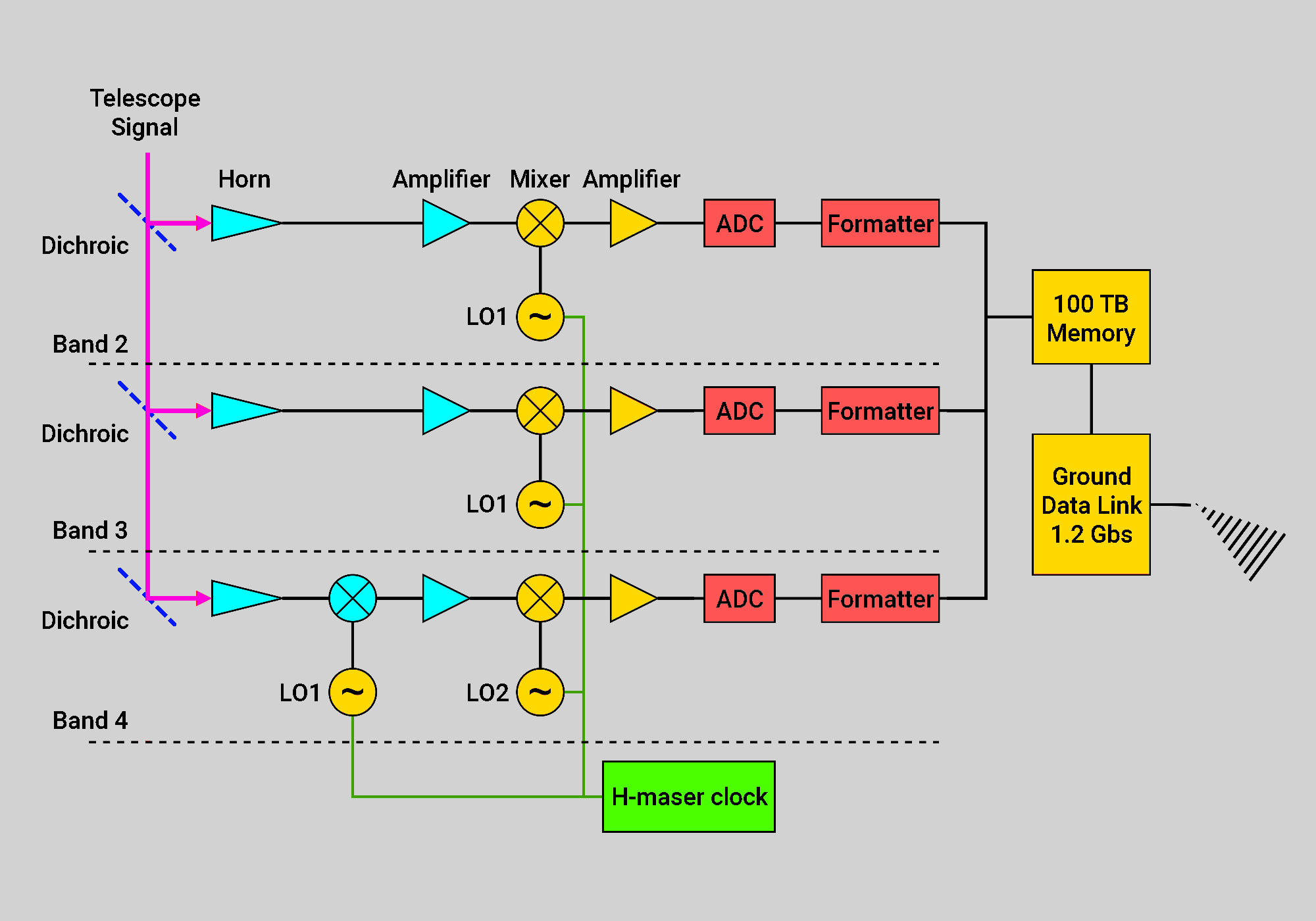
Device “Formator-P” acquires different types of data from various sources:
- along signals from VLBI receivers, simultaneously for upper and lower sideband in two polarizations;
- digital data from high resolutiion spectrometer through SpaceWire channel;
- digital data from high frequency, medium resolution spectrometer through SpaceWire channel;
- digital data from low frequency, medium resolution spectrometer through SpaceWire channel;
- digital scientific telemetry data through command/response data bus MIL-STD-1553B.
Digitized data from VLBI receivers get temporary stored in Flash-based nonvolatile memory - to accommodate very high-speed VLBI data rate to downlink data rate. Digital data, received through SpaceWire channel and MIL-STD-1553B data bus, combined with VLBI data, stored in nonvolateble memory, get coded with error-correcting codes, and then formatted to scientific data frame structure, for futher transmitting through two independent frequency channels to Earth stations.
⚡️ Results
During the project, high-tech equipment and scientific software were designed, manufactured and tested. The device “Formator-P” has been created, which has a number of unique technical features (Tab. 1).
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Size of Flash-based nonvolatile memory for VLBI data | 10000 Gbytes |
| Number of reserved analog inputs for VLBI signals | 4 |
| Bandwidth for VLBI signals | 5 - 975 MHz |
| Sampling frequency for VLBI signals | 2000 MHz |
| Number of bits per sample for VLBI signals ADC | 8 |
| Number of bits per sample for output VLBI signals | 1 or 2 |
| Maximum VLBI data rate, coming to nonvolatile memory | 16 Gbps |
| Number of reserved SpaceWire channels for receiving digital scientific data | 3 |
| Maximum data rate for SpaceWire channel | 25 Mbps |
| Number of reserved digital outputs to downlink transmitter device | 2 |
| Data rate for one digital output to downlink transmitter device | 600 Mbps |
| Maximum data rate for reserved MIL-STD-1553B | 500 Kbps |
| Supply voltage | +- 27 V |
| Power consumption (operating mode dependent) | 20 - 67 W |
| Dimensions | 330x310x81 mm |
⚡️ Fun fact
I had the honor of placing the company logo at the opening of the new office (Fig. 5).
As a young student, I sit on the right and create a finite element model of the ‘‘Formator-P’’ device for analyzing heat losses and generating heat power (Fig. 6).

